Research
- Research Topics
- Cell Biology and Tumor Biology
- Stem Cells and Cancer
- Inflammatory Stress in Stem Cells
- Experimental Hematology
- Molecular Embryology
- Signal Transduction and Growth Control
- Epigenetics
- Redox Regulation
- Vascular Oncology and Metastasis
- Clinical Neurobiology
- Molecular Neurogenetics
- Chaperones and Proteases
- Vascular Signaling and Cancer
- Molecular Neurobiology
- Mechanisms Regulating Gene Expression
- Molecular Biology of Centrosomes and Cilia
- Dermato-Oncology
- Pediatric Leukemia
- Tumour Metabolism and Microenvironment
- Personalized Medical Oncology
- Molecular Hematology - Oncology
- Cancer Progression and Metastasis
- Translational Surgical Oncology
- Neuronal Signaling and Morphogenesis
- Cell Signaling and Metabolism
- Cell Fate Engineering and Disease Modeling
- Cancer Drug Development
- Cell Morphogenesis and Signal Transduction
- Functional and Structural Genomics
- Molecular Genome Analysis
- Molecular Genetics
- Pediatric Neurooncology
- Cancer Genome Research
- Chromatin Networks
- Functional Genome Analysis
- Theoretical Systems Biology
- Neuroblastoma Genomics
- Signaling and Functional Genomics
- Signal Transduction in Cancer and Metabolism
- RNA Biology and Cancer
- Systems Biology of Signal Transduction
- Molecular thoracic Oncology
- Proteomics of Stem Cells and Cancer
- Computational Genomics and System Genetics
- Applied Functional Genomics
- Applied Bioinformatics
- Translational Medical Oncology
- Metabolic crosstalk in cancer
- Pediatric Glioma Research
- Cancer Epigenomics
- Translational Pediatric Sarcoma Research
- Artificial Intelligence in Oncology
- Neuropathology
- Pediatric Oncology
- Neurooncology
- Somatic Evolution and Early Detection
- Translational Control and Metabolism
- Soft-Tissue Sarcoma
- Precision Sarcoma Research
- Brain Mosaicism and Tumorigenesis
- Mechanisms of Genome Control
- Translational Gastrointestinal Oncology and Preclinical Models
- Translational Lymphoma Research
- Mechanisms of Leukemogenesis
- Genome Instability in Tumors
- Developmental Origins of Pediatric Cancer
- Brain Tumor Translational Targets
- Translational Functional Cancer Genomics
- Regulatory Genomics and Cancer Evolution
- SPRINT
- Cancer Risk Factors and Prevention
- Cancer Epidemiology
- Biostatistics
- Clinical Epidemiology and Aging Research
- Health Economics
- Physical Activity, Prevention and Cancer
- Preventive Oncology
- Digital Biomarkers for Oncology
- Genomic Epidemiology
- Cancer Survivorship
- Immunology and Cancer
- Cellular Immunology
- Molecular Oncology of Gastrointestinal Tumors
- T Cell Metabolism
- Translational Immunotherapy
- B Cell Immunology
- Immune Diversity
- Structural Biology of Infection and Immunity
- Applied Tumor-Immunity
- Neuroimmunology and Brain Tumor Immunology
- Adaptive Immunity and Lymphoma
- Immune Regulation in Cancer
- Systems Immunology and Single Cell Biology
- GMP & T Cell Therapy
- News
- Imaging and Radiooncology
- Radiology
- Research
- Computational Radiology Research Group
- Contrast Agents In Radiology Research Group
- Neuro-Oncologic Imaging Research Group
- Radiological Early Response Assessment Of Modern Cancer Therapies
- Imaging In Monoclonal Plasma Cell Disorders
- 7 Tesla MRI - Novel Imaging Biomarkers
- Functional Imaging
- Visualization And Forensic Imaging
- PET/MRI
- Dual- and Multienergy CT
- Radiomics Research Group
- Prostate Research Group
- Breast Imaging Research Group
- Bone marrow
- Musculoskeletal Imaging
- Microstructural Imaging Research Group
- Staff
- Patients
- Research
- Medical Physics in Radiology
- X-Ray Imaging and Computed Tomography
- Federated Information Systems
- Translational Molecular Imaging
- Medical Physics in Radiation Oncology
- Biomedical Physics in Radiation Oncology
- Intelligent Medical Systems
- Medical Image Computing
- Radiooncology - Radiobiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Molecular Radiooncology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Translational Radiation Oncology
- Molecular Biology of Systemic Radiotherapy
- Interactive Machine Learning
- Multiparametric methods for early detection of prostate cancer
- Molecular Mechanisms of Head and Neck Tumors
- Radiology
- Infection, Inflammation and Cancer
- Tumor Virology
- Viral Transformation Mechanisms
- Pathogenesis of Virus-Associated Tumors
- Immunotherapy and Immunoprevention
- Applied Tumor Biology
- Virotherapy
- Virus-associated Carcinogenesis
- Chronic Inflammation and Cancer
- Microbiome and Cancer
- Cell Plasticity and Epigenetic Remodeling
- Experimental Hepatology, Inflammation and Cancer
- Infections and Cancer Epidemiology
- Tumorvirus-specific Vaccination Strategies
- Mammalian Cell Cycle Control Mechanisms
- Molecular Therapy of Virus-Associated Cancers
- DNA Vectors
- Episomal-Persistent DNA in Cancer- and Chronic Diseases
- Other Units
- Cell Biology and Tumor Biology
- Research Groups A-Z
- Junior Research Groups
- Core Facilities
- Center for Preclinical Research
- Chemical Biology Core Facility
- Electron Microscopy
- Flow Cytometry
- Genomics and Proteomics
- Information Technology
- Library
- Kataloge -- Catalogues
- Zeitschriften - Journals
- E-Books - Ebooks
- Datenbanken - Databases
- Dokument-Lieferung - Document Delivery
- Publikationsdatenbank - Publication database
- DKFZ Archiv - DKFZ Archive
- Open Access
- Science 2.0
- Ansprechpartner - Contact
- More Information - Service
- Anschrift - Address
- Antiquariat - Second Hand
- Aufstellungssystematik - Shelf Classification
- Ausleihe - Circulation
- Benutzerhinweise - Library Use
- Beschaffungsvorschläge - Desiderata
- Fakten und Zahlen - Facts and Numbers
- Kooperationen, Konsortien - Cooperations, Consortia
- Kopieren, Scannen - Copying, Scans
- Kurse, Führungen - Courses, Introductions
- DKFZ-Intern - internal only
- DEAL-Info
- Light Microscopy
- Omics IT and Data Management Core Facility
- Small Animal Imaging
- Metabolomics Core Technology Platform
- Data Science @ DKFZ
- INFORM
- Baden-Württemberg Cancer Registry
- Cooperations & Networks
- National Cooperations
- International Cooperations
- Cooperational Research Program with Israel: DKFZ - MOST in Cancer Research
- Program
- Members of the Program Committee
- Call
- Publication Database
- German-Israeli Cancer Research Schools
- Archive
- Heidelberg - Israel, Science and Culture
- Symposium 40 Years of German-Israeli Cooperation
- 35th Anniversary Symposium
- 34th Meeting of the DKFZ-MOST Program
- 40th Anniversary Publication
- 30th Anniversary Publication
- 20th Anniversary Publication
- Flyer - The Cancer Cooperation Program
- List Publications 1976-2004
- Highlight-Projects
- Cooperational Research Program with Israel: DKFZ - MOST in Cancer Research
- Cooperations with industrial companies
- DKFZ PostDoc Network
- Cross Program Topic RNA@DKFZ
- Cross Program Topic Epigenetics@dkfz
- Cross Program Topic Single Cell Sequencing
- WHO Collaborating Centers
- DKFZ Site Dresden
- Health + Life Science Alliance Heidelberg Mannheim
Analysis of miRNA-impact on chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL)
project leader: Dr. Armin Pscherer, Dr. Daniel Mertensin collaboration with: group of Prof. Dr. Hartmut Doehner, PD Dr. Stephan Stilgenbauer, Division Internal Medicine III, University of Ulm
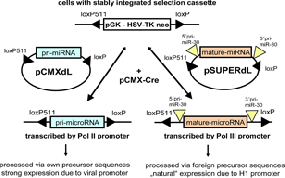
Fig.: Transgenesis-System for miRNA-Expression: RMCE (Recombinase-Mediated Cassette Exchange) Strategy. The selection cassette coded by the targeting vector is integrated randomly into the genome and selected by neomycin resistance to monclonality. Both expression vectors, Pol II- and Pol III-driven versions, were modified with the two respective lox-sites, obtaining the pCMXdL and pSUPERdL-versions („dL“ for „double Lox“). By cotransfection of a Cre-expression plasmid (pCMXhCre) and either a pCMXdL-PolII or a pSUPERdL-PolIII, the single-copy transgen between the loxP511- and loxP-sites is exchanged, selectable by an HSV-Tk counterselection with ganciclovir (GCV).
© dkfz.de
The goal of this project is the isolation of new or cell-type specific miRNAs from CLL-lymphomas and the identification of the miRNA target genes. For identification of target genes three different strategies are applied: the most common in-silicio prediction based on several algorithms is complemented by the transcriptome- and proteome-analysis of cells, which overexpress distinct miRNAs (Fig.). Therefore oligo-arrays are utilized for the expression-analysis and mass-spectrometry based quantification approaches via isototype-labelling are applied for proteom-analysis. The differential expression of distinct miRNAs in CLLs is tested for correlation with clinical parameters like prognosis, genomic aberrations, status of surrogate-markers and overall survival. Outstanding candidates of CLL-specific miRNAs will be ectopically expressed in CLL-cells to check for their potential of complementing the pathogen phenotype of CLL cells, like the sensitivity for the induction of apoptosis.

