Cancer Genome Research
- Functional and Structural Genomics

Prof. Dr. Holger Sültmann
Head of Division
The evolution of tumors is accompanied by molecular alterations on genomic, epigenomic, and gene expression levels. The aims of our research are to identify these molecular changes, to translate them into the diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of cancer at therapy response, and to understand their roles in the formation and progression of tumors.
Image: Research content Division Cancer Genome Research at DKFZ,
Image: Research content Division Cancer Genome Research at DKFZ,
Our Research
Our research comprises the genome-wide analysis of molecular alterations in various cancer entities with an emphasis on lung and breast tumors. To this end, we apply high-throughput technologies for DNA- and RNA-sequencing in tissues and blood samples („liquid biopsy“) and use the identified molecular markers for individual risk stratification and personalized clinical management of patients based on the tumor heterogeneity in space and time. To understand the roles of these molecular alterations in tumor progression and therapy resistance, we apply cellular 3D-coculture models as well as a variety of cell- and molecular biology methods.
Cancer cells differ from normal cells by their microenvironment, altered (epi)genomes, as well as gene and protein expression. The characterization of such changes in tumors and tumor stages is essential for understanding the mechanisms of tumor progression and the definition of molecular markers for diagnosis and prognosis. Tumor heterogeneity in space and time determines therapy success and patient survival. Therefore, we concentrate on precision medicine approaches in cancer research to address the following key questions:
tumor risk stratification with multimodal biomarkers
mechanisms of tumor progression and therapy failure
therapy response prediction using noninvasive approaches.
Projects
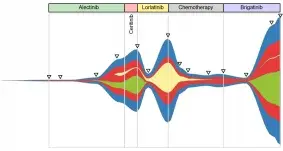
Liquid Biopsy for noninvasive tumor monitoring
Molecular tumor profiling is crucial for clinical practice, as the genomic composition of a tumor considerably influences its response to therapy. Typically, histopathological analysis of tissue samples is performed to determine the molecular properties of a tumor. However, tissue biopsies are invasive, may not accurately reflect tumor heterogeneity and provide little information about metastases.
Liquid biopsy analysis, in contrast to tissue biopsy, utilizes tumor-derived nucleic acids, proteins, or other molecules detected in body fluids, such as blood or urine. Sampling of such fluids is part of routine medical practice in certain cancers and is minimally invasive, with little risk for the patient. Furthermore, tumor material in a liquid biopsy sample may originate not only from the primary tumor but also from metastases, providing valuable insights into tumor heterogeneity.
We focus on the application of liquid biopsy to:
- identify new genomic biomarkers to monitor metastatic breast cancer (SATURN3)
- analyze epigenomic (DNA methylation) and genomic alterations (single nucleotide variants and copy number variants) to detect minimal residual disease and therapy resistance
- trace clonal compositional changes in cancer patients using molecular alterations in longitudinal blood samples
- predict therapy response and outcome by fragmentomic analysis of cell-free DNA
Further resources:
Tracking tumors through blood samples: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rpGLAdQBCdk
Methods for ctDNA detection and analysis: https://youtu.be/pwK1BTlQl6w
Cooperations:
- Dept. Thoracic oncology, Thoraxklinik Heidelberg
- Dept. Gynecological Oncology, NCT Heidelberg
- Dept. Molecular Genetics, DKFZ Heidelberg
- Multiparametric methods for early detection of prostate cancer, DKFZ and Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg
- Dept. Radio oncology, Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg
- Institute of Pathology, Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg
- Klinik für Hämatologie und Onkologie, Universitätsklinikum Schleswig-Holstein, Lübeck
Support: German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) in the funding programs German Centers for Lung Research (DZL), German Cancer Consortium (DKTK), OUTLIVE-CRC, and SATURN3
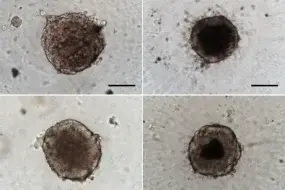
Modeling spatial heterogeneity and therapy resistance in lung cancer
Tumors exhibit significant heterogeneity in their cellular composition, making it essential to consider the tumor microenvironment, including cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), in the context of progression and response to treatment. To explore the impact of CAFs on the therapy resistance of tumor cells, we established 3D-co-culture models of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells with CAFs. Using a combination of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), epigenomic profiling, mass spectrometry-based proteomics, and metabolomics, we found that CAF-secreted factors impact lipid metabolism in ALK-rearranged tumor cells. In addition, we identified novel ligand-receptor interactions between CAFs and tumor cells.
Our current research focusses on the investigation of how the tumor microenvironment, including CAFs and immune cells, alters metabolic pathways in NSCLC and influences therapy resistance.
Cooperations: Thoraxklinik Heidelberg; Dept. of Pathology at Heidelberg University Medical Center
Support: German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) in the funding program German Center for Lung Research (DZL).
Team
The employees in the division have experience in molecular and cell biology, medicine, or AI-supported data analysis. Our goal is to investigate therapy resistance and translate molecular markers into clinical diagnostics.
-

Prof. Dr. Holger Sültmann
Head of Division
-

Dr. Isabell Berneburg
-

Prof. Dr. Petros Christopoulos
-

Simay Dolaner
-

Sabrina Gerhardt
-

Dr. Kate Glennon
-
Myesha Jahin
-

Dr. Florian Janke
-
Tamara Melanie Kokoschinski
-
Dr. Astrid Laut
-

Simon John Ogrodnik
-

Dr. Rebecca Schunk
-
Julie Surmely
-
Dr. Andrey Turchinovich
-
Silke Winter
Selected Publications
Janke, F, Gasser, M, Angeles, AK, Riediger, AL, Görtz, M, Appenheimer, L, Laut, AK, Ogrodnik, S, Gerhardt, S, Stenzinger, A, Schneider, MA, Thomas, M, Christopoulos, P, Sültmann, H
Angeles AK, Janke F, Daum AK, Reck M, Schneider MA, Thomas N, Christopoulos P, Sültmann H.
Janke F, Angeles AK, Riediger AL, Bauer S, Reck M, Stenzinger A, Schneider MA, Muley T, Thomas M, Christopoulos P, Sültmann H.
The ICGC/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium.
Get in touch with us







