Medical Physics in Radiology
- Imaging and Radiooncology

Prof. Dr. Mark Ladd
Head of Division and Coordinator of the Research Topic Imaging and Radiooncology
We develop innovative methods for imaging diagnostics and therapy in order to treat cancer patients better and more individually. Our research focuses on new technologies for MRI, PET and optical tomography to obtain important information about tumors and metastases in a non-invasive and gentle manner. In collaboration with clinical partners, our researchers are working on integrating these methods into routine care.
Image: 3D mapping of intracellular pH in a brain tumor patient using phosphorus-31 MR spectroscopic imaging at 7 Tesla (method according to Korzowski A et al., 2020, Magn Reson Med, 84:1707-1723). Interpolated pH map overlaid on a clinical contrast-enhanced MRI image., © dkfz.de
![3D mapping of intracellular pH in a glioma patient [Translate to English:] 3D mapping of intracellular pH in a glioma patient](/fileadmin/_processed_/5/4/csm_B%C3%BChnenbild_7f656718ad.webp)
Image: 3D mapping of intracellular pH in a brain tumor patient using phosphorus-31 MR spectroscopic imaging at 7 Tesla (method according to Korzowski A et al., 2020, Magn Reson Med, 84:1707-1723). Interpolated pH map overlaid on a clinical contrast-enhanced MRI image., © dkfz.de
Our Research
The Division of Medical Physics in Radiology develops new methods for imaging-based diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
Our research focuses on novel hardware as well as software-based acquisition and reconstruction strategies for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and optical tomography.
We strive to improve and individualize cancer patient treatment by acquiring quantitative biomedical information about tumors and metastases with non-invasive imaging methods. For example, we are expanding the diagnostic value of MRI by using very powerful magnetic fields (7 or 9.4 Tesla) to depict the distribution of sodium, oxygen, potassium, and chlorine inside the body. Another approach to capture metabolic processes is hyperpolarization of carbon in various chemical substrates, which are then injected into the body and measured with MRI. By optimizing MRI diffusion techniques, we have been able to greatly improve the diagnostic accuracy of breast cancer screening, and we are investigating how maps of tissue susceptibility correlate with disease. An additional emerging MR imaging contrast is provided by Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) imaging, which allows detection and measurement of glucose or mobile proteins. Furthermore, we are exploring new detector concepts for simultaneous PET and optical imaging.
Medical imaging continues to be one of the key technologies for cancer detection, characterization, and therapy monitoring. Despite the enormous technological advances achieved in the past decades, imaging still has enormous potential to reveal more information about the metabolic, physiologic, and functional parameters of tumors and metastases. This information can then be used to choose the best therapy for each individual patient. In collaboration with clinical divisions of the DKFZ and partners at the university hospital, we are working to translate our developments into standard patient use. This includes state-of-the-art imaging protocols at our MR imagers located at the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT).
Picture Gallery
-

8-channel antenna array for 3T MRI. Designed and built at the DKFZ -

View into a 3T MRI radiofrequency amplifier. Designed and built at the DKFZ -
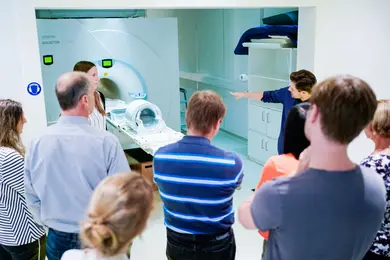
Guided tour at the 7 Tesla MR scanner during the Night of Research -

23Na body coil for the application at 7 Tesla, developed and built at the DKFZ. -
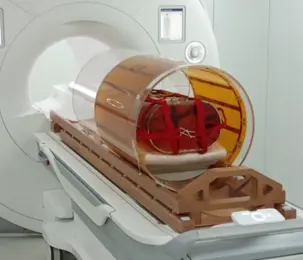
An essentially radiation-transparent body coil integrated with a patient rotation system for MR-guided particle therapy. -

Girls' and Boys' Day: A visit to the 7T MRI
Research Groups
Our research group develops non-invasive metabolic and molecular MR techniques using 1H and X nuclei, comprising high-resolution NMR spectroscopy (MRS) and MR spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) at ultra-high fields (B0 ≥ 7T) and chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MR imaging. A particular clinical research focus is the molecular tissue characterization of brain tumors for the stratification of genetic subtypes and the assessment of response to therapies. Another focus is the development of novel imaging techniques for the improved molecular characterization of breast cancers.
More information here.
Our research group explores hyperpolarized carbon-13 magnetic resonance to overcome the fundamental sensitivity limits of conventional MR, using dissolution Dynamic Nuclear Polarization to assess metabolic and physiological parameters in real time. Following the administration of hyperpolarized substrates such as [1-¹³C]pyruvate, cellular metabolism transfers the ¹³C label to downstream products, each with a distinct resonance frequency, enabling dynamic tracking of key pathways such as pyruvate-to-lactate conversion.
Our work uses preclinical models in oncology and neuroscience, ranging from controlled in vitro systems, including cellular models, to small-animal studies using the SpinAligner platform. We also focus on advancing fast and quantitative ¹³C MR sequence strategies and developing new molecular probes to broaden the available probe repertoire. Alongside these preclinical efforts, we pursue the clinical translation of hyperpolarized ¹³C MR using the SpinLab platform, advancing its use for clinical applications in oncology and neuroscience.
More information here.
Our research group is set up to improve and enhance the diagnostic value of emission tomographic imaging systems as specifically related to cancer. These include the nuclear medicine imaging modalities positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) both for clinical and for preclinical applications. With a focus on preclinical imaging in small animals these also include the optical modalities bioluminescence imaging (BLI) as well as fluorescence mediated imaging (FMI) and fluorescence diffusion optical tomography (DOT).
More information here.
The research group focuses on MR proton imaging in humans at ultrahigh field (UHF) of 7 Tesla with a special interest in body imaging at this field strength. Due to the short radiofrequency (RF) wavelength, the spatial distribution of the magnetic component of the RF field (B1+), which is necessary for the imaging process, is highly inhomogeneous. This yields inhomogeneous signal and contrast distributions in the body (see Figure), making a diagnosis difficult or impossible. To counteract this effect, we use multi-transmit (Tx) body coils in combination with parallel transmission (pTx) techniques and dedicated RF pulses.
More information here.
Our research group develops multichannel transmit systems for use in ultra-high field MRI systems to facilitate imaging of large volumes in the human body. We aim to provide tools that allow clinicians to make use of the full potential of ultra-high field MRI.
More information here.
Using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the diffusion process of water molecules in biological tissue can be observed. Since the diffusional motion is restricted by barriers such as cell membranes, the measured diffusion coefficients are indirectly related to the cellular structure. Therefore, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is extensively used to gain insights into the structure of biological tissues, especially in the area of tumor and stroke diagnosis or to reconstruct white matter tracts in the human brain.
More information here.
The research area of the project group focuses on the evaluation of RF exposure of persons during MR examinations at static field strengths from 7 up to 14 Tesla (ultra-high field MRI). This includes in particular the simulation-based development and optimization of innovative multi-channel transmitter coils with the aim of reduced RF exposure with homogeneous nuclear spin excitation. Further research areas are the development of anatomical body models, the evaluation of SAR and temperature limits, the implementation of thermal regulation systems for realistic safety assessment and simulation-based compatibility tests of passive medical implants. Our group provides also consultancy on MR safety issues.
More information here.
To provide optimum outcome for patients, accurate and safe delivery of therapeutic procedures is mandatory. Image guidance enables visualization of targets and organs at risk. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides excellent soft tissue contrast and allows for non-invasive monitoring of crucial parameters during treatment (e.g., organ size and position, filling of organs, or respiratory motion, etc.). Therefore, MRI is excellently suitable for guidance of therapies, such as radiotherapy with photons or particles. The aim of this project group is to develop MR imaging hardware and methods, to enable and improve guidance of therapeutic methods.
More information here.
Besides conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), where the magnetization of 1H nuclei is measured, other atomic nuclei with spin I > 0 can be used for signal detection. These nuclei are called X-nuclei. In our department we are developing hardware as well as acquisition, reconstruction and post-processing methods to acquire in-vivo MR signals of sodium (23Na), potassium (39K), chloride (35Cl), oxygen (17O), magnesium (25Mg), phosphorus (31P) and carbon (13C).
More information here.
Our project group is dedicated to maximizing the potential of 7 Tesla MRI for human proton (1H) imaging, aiming to achieve unprecedented levels of detail and sensitivity. We pursue this goal through the active development of novel hardware components and innovative RF management strategies. Furthermore, we optimize existing imaging methods – focusing on image contrast, artifact reduction, and SNR efficiency – to address the unique technical challenges inherent in operating at such high field strengths.
More information here.
The "Electronics & Embedded Systems" working group is a service group for the DKFZ's research focus “Imaging and Radiation Oncology”. We provide the link to different scientific groups to realize technical projects. Our expertise lies in system architecture and design of electro-mechanical systems, real-time capable embedded and control systems, such as PLC and FPGA solutions, PLC design and medical engineering.
Mor information here.
Selected Projects
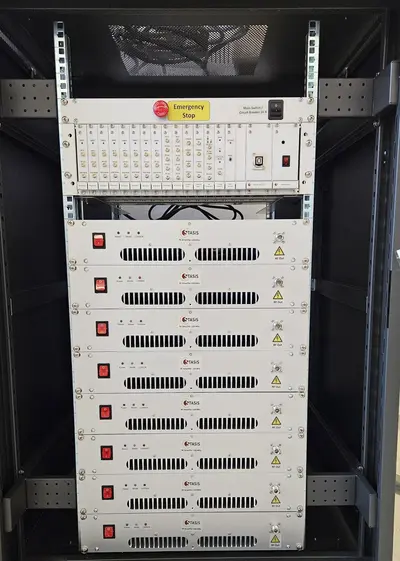

Standardisation for safe implant scanning in MRI
Within the STASIS project (www.ptb.de/stasis), we are leading work package 2 - reference hardware. In this sub-project, a multi-channel reference transmission system for testing implants is to be realized. The test system consists of an 8-channel array the size of a transmitting body coil for an MRI system, a system for generating 8 independent waveforms and 8 amplifiers with 1000 W power per channel. In addition, there is a simple graphical user interface for operation. All plans for the entire system as well as the software are published under an open source license.
32-channel transmitting system
As part of the MRexcite project, the DKFZ's 7T device was expanded to 32 transmission channels and equipped with an integrated 32-channel transmission antenna. As part of the project, the system is being tested for its usability for research and clinical use and continuous improvements are being made.
Within the EU-funded MIRACLE project an add-on device for 7T MRI scanners is developed that determines the efficacy of chemotherapy in breast cancer patients after one to two round of chemotherapy. In current practice patients receive six rounds of chemotherapy before efficacy can determined based on tumor size. In over 30% of patients tumors do not shrink meaning that chemo is ineffective, and the chemotherapy is stopped, and other treatments might be started. The MIRACLE coil determines efficacy sooner based on biomarkers. This leads to an improved Quality of Life in patients, it enables caregivers to change to other treatment strategies faster, and reduces health care costs.
More information about the project here www.wavetronica.com/projects/miracle-project/.
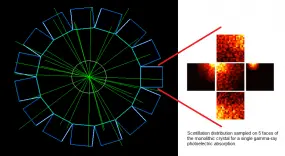
This project seeks to contribute to the advancement of PET instrumentation and the development of novel multimodal techniques. From preclinical systems to whole-body clinical systems a focus is drawn on investigating monolithic-detector design primarily through the use of computational simulations and with the support of basic experimental tests. The simulation approach includes the full simulation of scintillation photons within the crystals and therefore constitutes a powerful tool being used to optimise the co-dependent scanner geometrical design and the applied gamma-ray point-of-interaction determination algorithm. A prototype for a multimodal preclinical scanner integrating PET imaging with optical tomography is currently being developed using said tools.
Teaching

More information about our seminars and the opportunity to write a bachelor or master thesis in our department are here.
Medical Physics Seminar

The Medical Physics Seminar provides overview talks regarding current status of research and specialized talks concerning advanced topics. This seminar is offered in every term. In the summer term, the seminar ist held by the Division Medical Physics in Radiation Oncology (E040). In the winter term the Division Medical Physics in Radiology administers this seminar on the topic: Radiological Imaging (MRI/CT/PET). More information can be found here.
Team
The Department of Medical Physics in Radiology is divided into various working groups.
- Show profile

Prof. Dr. Mark Ladd
Head of Division and Coordinator of the Research Topic Imaging and Radiooncology
-

Dr. Helen Abeln
Group leader
-

Marcel Awenius
PhD student
-
Prof. Dr. Peter Bachert
-
Renate Bangert
Technician
-
Leonie Bartos
-
Ute Beutel
Student assistant
-
Frauke Birkenstock
-
Prof. Dr. Andreas Bitz
-
Tabita Charlotte Bomhard
Student assistant
-

Dr. Philip Boyd
Group leader CEST Imaging
-
Petr Bulanov
PhD student
-
Seraphin Bücklers
Student assistant
-
Silke Cardona
Secretary Research Topic Imaging and Radiooncology
-

Furkan Cetin
M.Sc. student
-

Mirija Class
M.Sc. student
-
Dhritman Dhar
Student assistant
-

Dr. Thomas Fiedler
Group leader
-

Dr. Vanessa Franke
Group leader MR spectroscopy
-
Lucas Freitag
M.Sc. student
-
Kathrin Ute Gerbig
-
Max Gorenflo
PhD student
-

Alissa Greshake
Secretary
-

Dr. Johannes Grimm
Research scientist
-

Oliver Gödicke
PhD student
-
Valentin Hahn
M.Sc. student
-
Emil Hain
-
Pablo Jimenez
PhD student
-
Dr. Stefan Kegel
Scientific support
-
Neele Kempa
PhD student
-
Jan Kesting
M.Sc. student
-
Christian Kindtner
Technical assistant
-
Dr. Dorde Komljenovic
-
Lennart Alexander Kopp
B.Sc. student
-

Dr. Andreas Korzowski
Project Coordination MAMMACARE and MIB2
-
Florian Kroh
-

Priv. Doz. Dr. Tristan Anselm Kuder
Group leader & Deputy Head of Division
-
Jana Lechner
M.Sc. student
-

Dr. Alexandra Lipka
Group leader
-

Ignacio Nicolás Lopez Martinez
PhD student
-

Jana Losch
PhD student
-
Franziska Masuch
PhD student
-

Dr. Petr Menshchikov
Research scientist
-
Una Molnar
-
Melanie Müller
Technician
-
Prof. Dr. Armin Nagel
-

Dr. Stephan Orzada
Group leader
-
Bastian Ott
B.Sc. student
-

Dr. Jörg Peter
Group leader
-
Andrea Pino Ramos
PhD student
-

Justyna Platek
PhD student
-

Dr. Tanja Platt
Group leader
-
Julian Rauch
-

Dr. Anna Scheipers
Research scientist
-
Mirjam Schleske
PhD student
-

Dr. Simon Schmidt
Group leader
-
Sebastian Schmitter
Group leader
-
Jan-Philipp Schmitz
PhD student
-
Bela Seng
M.Sc. student
-
Anton Stahl
PhD student
-
Maximilian Stucke
M.Sc. student
-
Linda Stützle
B.Sc. student
-
Moritz Thierfeld
M.Sc. student
-
Dr. Reiner Umathum
Research scientist
-

Francesca Vacca
PhD student
-
Yuting Wang
PhD student
-
Valentin Wegener
-
Maximilian Kaspar Widmer
B.Sc. student
-
Jannis Wirtz
M.Sc. student
-

Jinyang Yu
PhD student
-

Henrik zu Jeddeloh
PhD student
Selected Publications
Fiedler TM, Orzada S, Flöser M, Rietsch SHG, Schmidt S, Stelter JK, Wittrich M, Quick HH, Bitz AK, Ladd ME
Kroh F, von Knebel Doeberitz N, Breitling J, Maksimovic S, König L, Adeberg S, Scherer M, Unterberg A, Bendszus M, Wick W, Bachert P, Debus J, Ladd ME, Schlemmer H-P, Korzowski A, Goerke S, Paech D
Ladd ME, Quick HH, Speck O, Bock M, Doerfler A, Forsting M, Hennig J, Ittermann B, Möller HE, Nagel AM, Niendorf T, Remy S, Schaeffter T, Scheffler K, Schlemmer H-P, Schmitter S, Schreiber L, Shah NJ, Stöcker T, Uder M, Villringer A, Weiskopf N, Zaiss M, Zaitsev M
Awenius M, Abeln H, Müller M, Franke VL, Rincon G, Glowa C, Schmitt M, Bangert R, Ludwig D, Schmidt AB, Kuder TA, Ladd ME, Bachert P, Biegger P, Korzowski A
News

Current information and news from the department can be found here.
Get in touch with us


