7 Tesla Multinuclear MRI
Gaining Additional Insights via MR Imaging of Further Nuclei besides Hydrogen

Besides conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), where the magnetization of 1H nuclei is measured, other atomic nuclei with spin I > 0 can be used for signal detection. These nuclei are called X-nuclei. In our department we are developing hardware as well as acquisition, reconstruction and post-processing methods to acquire in-vivo MR signals of sodium (23Na), potassium (39K), chloride (35Cl), oxygen (17O), magnesium (25Mg), phosphorus (31P) and carbon (13C). Investigations of these nuclei are of special interest in clinical research because of their crucial role in many cellular processes. For instance, 23Na, 39K, and 35Cl concentrations strongly depend on the physiologic condition of a cell. And 17O MRI can be used to directly access the oxygen consumption non-invasively.
Research Topics
- Exploring new and improving existing multinuclear imaging hardware, pulse sequences, reconstruction and post-processing methods
- Determination of ion concentrations, e.g. [23Na+], [39K+], [35Cl-]
- Assessment of cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption via 17O MRI
- Clinical translation of imaging techniques developed in the group
X-nuclei are physiologically relevant nuclei with a nuclear spin I > 0, which can thus be used for signal detection in addition to hydrogen. The requirements for X-nuclei imaging are strongly associated with their atomic properties. Due to the nucleus-specific gyromagnetic ratio the different nuclei have differing resonance frequencies at 7 Tesla (1H: ca. 297 MHz, 23Na: ca. 79 MHz, 35Cl: ca. 29 MHz, 39K: ca. 14 MHz). As a result, the MR scanner must support these frequencies in addition to the proton frequency and special coils are required for the respective nuclei (e.g. 23Na head coil, 23Na body coil). In collaboration with the research groups '7 Tesla MR: RF Systems and Concepts' and 'Electromagnetic Simulations and RF Safety' we are developing and building MR coils for X-nuclei imaging in-house such as a sodium body coil (Platt et al., Magn Reson Med, 2018).
Furthermore, 17O, 23Na, 39K, and 35Cl have a nuclear spin greater than 1/2 and thus exhibit very short relaxation times. This necessitates the use of dedicated pulse sequences such as a density-adapted radial sequence (Nagel et al., Magn Reson Med, 2009). Furthermore, the in vivo concentration of X-nuclei is orders of magnitude lower compared to the concentration of 1H. X-nuclei imaging therefore greatly benefits from ultrahigh static magnetic fields such as 7 Tesla and X-nuclei MR investigations can be further improved via advanced image reconstruction and post-processing techniques.
References:
- Gast LV, Platt T, Nagel AM, Gerhalter T: Recent technical developments and clinical research applications of sodium (23Na) MRI. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 2023.
- Platt T, Ladd ME, Paech D: 7 Tesla and beyond: advanced methods and clinical applications in magnetic resonance imaging. Investigative radiology. 2021; 56:705-725.
- Kratzer FJ, Flassbeck S, Schmitter S, Wilferth T, Magill AW, Knowles BR, ... & Nagel AM. 3D sodium (23Na) magnetic resonance fingerprinting for time‐efficient relaxometric mapping. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2021; 86(5):2412-2425.
- Kratzer FJ, Flassbeck S, Nagel AM, Behl NGR, Knowles BR, Bachert P, ... & Schmitter S. Sodium relaxometry using 23Na MR fingerprinting: A proof of concept. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2020; 84(5):2577-2591.
- Lott J, Platt T, Niesporek SC, Paech D, Behl NGR, Niendorf T, ... & Nagel AM. Corrections of myocardial tissue sodium concentration measurements in human cardiac 23Na MRI at 7 Tesla. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2019; 82(1): 159-173.
- Niesporek SC, Nagel AM, & Platt T. Multinuclear MRI at ultrahigh fields. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2019; 28(3):173-188.
- Platt T, Umathum R, Fiedler TM, Nagel AM, Bitz AK, Maier F, Bachert P, Ladd ME, Wielpütz MO, Kauczor HU, Behl NGR: In vivo self-gated 23Na MRI at 7 T using an oval-shaped body resonator. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2018; 80:1005-1019.
- Nagel AM, Laun FB, Weber MA, Matthies C, Semmler W, Schad LR. Sodium MRI using a density-adapted 3D radial acquisition technique. Magn Reson Med 2009; 62(6):1565-1573.

Visualization of the Energy Metabolism: Oxygen-17 (17O) MR Imaging
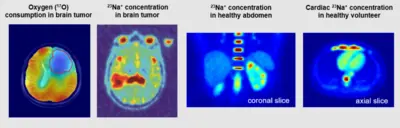
Dynamic 17O MRI utilizes the stable and MR-detectable oxygen isotope (17O) to quantify the functional parameter of the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (CMRO2), reflecting the energy metabolism in the human brain. The CMRO2 parameter is an indicator of cell viability. In many diseases such as Parkinson’s or in Alzheimer’s disease or cancer (‘Warburg Effect’) CMRO2 is reduced and might therefore be an important diagnostic parameter. The method, which includes inhalation of 17O2 gas, was first validated in a volunteer study, where we could verify our results and show reproducibility (Niesporek et al. Magn Reson Med 2018). Measuring various glioma patients demonstrated the capability of dynamic 17O MRI for direct metabolic imaging generating a functional contrast between healthy and malignant tissue (Paech et al. Radiology 2020). Moreover, this complex method was applied in a first patient with early subacute stroke (Ebersberger et al. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2023).
References:
- Ebersberger L, Kratzer FJ, Potreck A, Niesporek SC, Keymling M, Nagel AM, ... Paech D & Platt T. First application of dynamic oxygen-17 (17O) magnetic resonance imaging at 7 Tesla in a patient with early subacute stroke. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2023.
- Paech D, Nagel AM, Schultheiss MN, Umathum R, Regnery S, Scherer M, ... & Niesporek SC. Quantitative dynamic oxygen 17 MRI at 7.0 T for the cerebral oxygen metabolism in glioma. Radiology 2020; 295(1): 181-189.
- Niesporek SC, Umathum R, Lommen JM, Behl NGR, Paech D, Bachert P, Ladd ME, Nagel AM. Reproducibility of CMRO2 determination using dynamic (17) O MRI. Magn Reson Med 2018; 79(6):2923-2934.
- Niesporek SC, Umathum R, Fiedler TM, Bachert P, Ladd ME, Nagel AM. Improved T2* determination in 23Na, 35Cl, and 17O MRI using iterative partial volume correction based on 1H MRI segmentation. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics, Biology and Medicine 2017:1-18.
- Niesporek SC, Hoffmann SH, Berger MC, Benkhedah N, Kujawa A, Bachert P, Nagel AM. Partial volume correction for in vivo (23)Na-MRI data of the human brain. Neuroimage 2015; 112:353-363.
- Hoffmann SH, Radbruch A, Bock M, Semmler W, Nagel AM. Direct (17)O MRI with partial volume correction: first experiences in a glioblastoma patient. MAGMA 2014; 27(6):579-587.
- Hoffmann SH, Begovatz P, Nagel AM, Umathum R, Schommer K, Bachert P, Bock M. A measurement setup for direct 17O MRI at 7 T. Magn Reson Med 2011;66(4):1109-1115.
- Nagel AM, Laun FB, Weber MA, Matthies C, Semmler W, Schad LR. Sodium MRI using a density-adapted 3D radial acquisition technique. Magn Reson Med 2009; 62(6):1565-1573.
Contact
-

Dr. Tanja Platt
Group leader