Pathogenesis of Virus Associated Tumors
- Immunology, Infection and Cancer

Prof. Dr. Henri-Jacques Delecluse
Group Leader
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects the large majority of the population and is responsible for 1 to 2% of all cancers. Our projects aim at understanding how the virus induces these tumors.
Our Research
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects the large majority of the population and is responsible for 1 to 2% of all cancers. EBV is also responsible for the development of infectious mononucleosis (IM), a frequent and potentially debilitating infectious syndrome. Recent epidemiological studies have demonstrated that EBV plays a major role in the development of auto-immune diseases, in particular multiple sclerosis. Finally, it is one of the last tumor viruses for which neither a preventative vaccine not a curative treatment is available.
Our projects aim at understanding how the virus induces these tumors. We previously found that the multiple microRNAs encoded by the virus modulate its oncogenic properties (Lin et al., PLoS Path 2015; Bernhardt et al., PLoS Path 2016; Haar et al., NAR 2016). We then moved our attention to the role of viral variants in the development of cancers (Li et al., Nature Microbiology 2019; Tsai et al., Cell reports 2015). Indeed, some EBV-associated tumors such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma and Burkitt’s lymphomas have a strikingly heterogeneous geographic distribution. We have shown that some of these differences can be explained by the infection with particular types of Epstein-Barr viruses.
Another interesting question is the contribution of lytic replication, the process that leads to the production of viruses, to cancer development and. We showed that the EBV infectious particles can deregulate the centrosome machinery and induce genetic instability (Shumilov et al., Nature Comm 2017). This newly identified cancer risk is independent of the viral genome and could significantly expand the range of diseases caused by the virus.
More recently, we have embarked on a collaborative project to study the role played by EBV in the development of the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis. We will study the interactions between the virus and the host, with a focus on the role of polymorphisms, both viral and cellular, and how they influence the immune response against the virus.
We have also developed a new type of immunotherapy that is based on antibodies that recognize surface proteins on tumor cells that are combined with viral antigens. The antibody moiety bids to the tumor cells, allowing the internalization of the viral antigens. These in turn are loaded on MHC class II molecules, allowing recognition of the tumor cells by T cells specific for the viral antigen. These antigen-loaded antibodies, or AgAbs have demonstrated their efficacy in a model of lymphoma in vitro. Since then we have obtained evidence of efficacy and safety in an animal model of acute myeloid leukemia.
Future outlook
While we will continue our projects on the molecular mechanisms of EBV-induced cancer, we will develop a new project on the role of EBV in the development of multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases. Another priority will be the further development of immunotherapeutic strategies based on antigen-loaded antibodies.
Projects
Team Leader: Dr. Chih-Ying Lee
Team members: Hao Li, Millie Robinson, Guangsen Pan
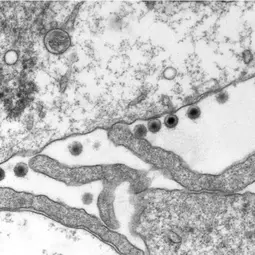
Infections with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) are associated with cancer development, and EBV lytic replication, the process that generates virus progeny is a strong risk factor for some cancer types. We have recently reported that EBV infection of B-lymphocytes in vitro and in a mouse model leads to an increased rate of centrosome amplification (Figure 1), associated with chromosomal instability. Importantly, this effect can be reproduced with virus-like particles devoid of EBV DNA, but not with defective virus-like particles that cannot infect host cells because they lack a glycoprotein involved in target cell entry.
We could first identify the viral tegument protein BNRF1 as an inducer of centrosome amplification though over-duplication of the centrosome machinery. EBV mutants that lack BNRF1 have lost this property but it can be restored by reintroduction of the BNRF1 protein into the virus particle. Importantly, BNRF1 localizes to the centrosome compartment in transfected cells. This identifies a new mechanism by which EBV particles can induce chromosomal instability without establishing a chronic infection, thereby conferring a risk for development of tumors that do not necessarily carry the viral genome.
Current projects look at the contribution of other EBV proteins to the development of genetic instability and how they interact with the cell machinery to cause these abnormalities.
Team leaders: Dr. Francesco Baccianti, PD Dr. Susanne Delecluse
Team members: Nicole Feichtgruber, Jonathan Till Abele, Inès Ruxer
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurological disease in which the immune system irreversibly damages the myelin layer in the brain and spinal cord, potentially leading to serious consequences such as paralysis or severe visual impairment. Recent work by Bjornevik and colleagues (Bjornevik et al., Science 2022) has demonstrated the causal link between EBV infection and the development of multiple sclerosis, confirming previous reports that showed infectious mononucleosis as a risk factor for MS. However, despite the many proposed roles played by EBV in the pathogenesis of this neurodegenerative autoimmune condition, limited evidence is currently available.
Our laboratory, in partnership with other 10 research groups across Europe, has received funding in the frame of the Horizon Europe Programme to shed new light on how EBV interaction with the host can promote the development of MS. The BEHIND MS Consortium, with our group as coordinator, by bringing together complementary expertise, will investigate in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo the mechanisms underlying the pathogenic role of EBV in multiple sclerosis, with the goal of identifying new druggable therapeutic targets and biomarkers to improve diagnose, staging and treatment of this yet-incurable disease.

Team leader: PD Dr. Susanne Delecluse
Team members: Qipeng Hu, Shuang Yang
Patients with an immunodeficiency, and in particular transplant recipients, have a reduced ability to control infectious agents. In the presence of a diminished functional T cell response, a substantial proportion of individuals who were previously infected with EBV cannot prevent infected B cells from resuming proliferation (Figure 1). Transplant recipients, in particular children, who undergo primary infection whilst already under immunosuppressive treatment carry an even higher risk of EBV-associated diseases like post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD). We have previously studied the viral strains that are found in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinomas and gastric carcinomas and found that these strains exhibit specific properties (Tsai et al. Cell reports 2013, Shumilov, Tsai et al Nature comm. 2017). We are now exploring the hypothesis that the risk of PTLD is linked with infections with EBV strains endowed with higher transforming abilities. We have recruited a collective of patients with EBV reactivation after transplantation and have established cell lines infected with EBV from their peripheral blood. We aim to study multiple parameters such as viral and cellular protein implicated in EBV-mediated transformation and microRNA expression in primary cells and in the cell lines that were established from these patients.
This project results from a close cooperation with the Kidney Center Heidelberg e.v., the Department of Haematology as well as the Institute of Virology from the University of Heidelberg.
Team leader: Dr. Guillaume Wassmer
Team members: Elise Dondelot, Shutao Ma
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) accounts for 80% of acute leukemia cases in adults and results from the accumulation of immature malignant myeloid cells at the expense of healthy differentiated counterparts. The treatment options for AML remain limited. While a moderate therapy success has been observed in patients below the age of 65, about 70% of older patients succumb to the disease within one year after diagnosis. Therefore, the search for more therapeutic options in AML is imperative.
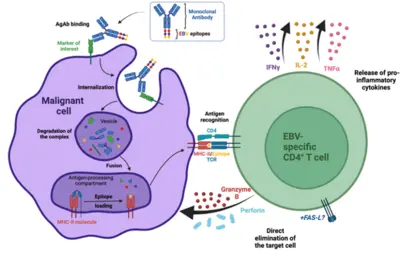
Our laboratory has developed a platform for efficient delivery of immunodominant viral epitopes to tumor cells. The approach is based on antigen-armed antibodies (AgAbs) that carry antigens from the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). With the help of this strategy, malignant cells become visible for the immune system and are targeted by EBV-specific CD4+ cytotoxic T cells. Indeed, AgAbs bind to surface molecules expressed by the malignant cells and provoke receptor-mediated endocytosis. As a result, viral peptides included in the AgAbs are shuttled into the endosomal compartments of the target cells, where the epitopes can be processed for MHC class II-restricted presentation on the cell surface. In EBV-positive individuals, circulating memory virus-specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cells recognize the MHCII-bound peptides on the surface of tumor cells and mediate cell lysis.
We have developed AgAbs that specifically target AML and leukemia stem cells. This approach makes sense because a high percentage of AML cells express functional MHC-II molecules and up-regulate several specific membrane receptors. Our preliminary experiments suggest that the AgAb strategy in AML is promising. Indeed, AgAbs can eliminate primary AML cells in vitro and ex vivo. Moreover, this therapeutic approach conferred a strong survival advantage in a murine AML model.
News and media coverage

In February, Inès Ruxer joined our group as a PhD student becoming the last member of the BEHIND-MS Team. Together with Jonathan Till Abele and Nicole Feichtgruber she will be investigating the complex interactions between EBV-infected B cells and the other cellular components of the central nervous system.

On November 14th and 15th we hosted the first Annual Meeting of the BEHIND-MS project. This was a great occasion for the consortium partners to discuss in person the results of this first year of work, as well as to plan the work for the years ahead. The meeting was also attended by the members of the BEHIND-MS Adivisory Board including Ms. Jana Hlavacova, the patient representative from E.M.S.P.
Read more about the meeting here
Jonathan Till Abele and Nicole Feichtgruber have joined the lab as PhD students. With their PhD projects, funded through the BEHIND-MS Consortium, they will try to understand how EBV-infected B cells can interact with other immune cells, endothelial cells, glia and neurons, ultimately reshaping the microenvironment of the central nervous system.
Team
- Show profile

Prof. Dr. Henri-Jacques Delecluse
Group Leader
- Show profile

Jonathan Till Abele
PhD student
- Show profile

Dr. Francesco Baccianti
Postdoctoral scientist
- Show profile

Bowen Bai
PhD student
- Show profile
Dr. Susanne Delecluse
Clinical scientist, Group Leader NZ/DKFZ Cooperation Unit
- Show profile
Elise Dondelot
PhD student
- Show profile

Nicole Feichtgruber
PhD student
- Show profile

Gesa Frese
Project Manager, BEHIND-MS Consortium
- Show profile

Jasmin Fuchs
Technician
- Show profile

Qipeng Hu
PhD student
- Show profile
Difei Hu
Bachelor student
- Show profile

Dr. Chih-Ying Lee
Postdoctoral scientist
- Show profile

Hao Li
PhD student
- Show profile

Helge Lips
Technician
- Show profile

Shutao Ma
PhD student
- Show profile
Louna Oviève
MD student
- Show profile

Guangsen Pan
PhD student
- Show profile

Remy Poirey
Scientific employee
-
Timo Quarneti
- Show profile

Millie Robinson
PhD student
- Show profile
Ines Ruxer
PhD student
- Show profile

Dr. Guillaume Wassmer
Postdoctoral scientist
- Show profile

Shuang Yang
PhD student
Opportunities
Postdoctoral researchers interested in working in our group should apply for the DKFZ International Postdoc Program or similar funding opportunities and get in contact with Prof. Delecluse directly.
Clinician Scientists interested in working in our group should apply for the DKFZ Clinician Scientist Program and get in contact with Prof. Delecluse directly.
Open positions will be directly advertised on this page and on the DKFZ webpage.
Highly motivated and prepared students interested in pursuing a PhD in our research group should apply for the DKFZ International PhD program or similar funding opportunities. Please contact the Team Leaders of the single projects directly for more information.
Open positions will be directly advertised on this page and on the DKFZ webpage.
Candidates for the CSC Scholarships should get in touch with Dr. Chih-Ying Lee and Prof. Delecluse for further information.
Students interested in working in our research group for a minimum of 2 months should apply directly with the Team Leaders of the projects of interest including information about their academic CV, purpose of the internship, and expected length of the internship.
Medical students interested in a MD thesis in our group should directly contact PD Dr. Susanne Delecluse.
Selected Publications
Baccianti F, Masson C, Delecluse S, Li Z, Poirey R, Delecluse H-J
Li Z, Tsai MH, Shumilov A, Baccianti F, Tsao SW, Poirey R, Delecluse HJ
Schneidt V, Ilecka M, Dreger P, van Zyl DG, Fink S, Mautner J, Delecluse HJ
Shumilov A, Tsai MH, Schlosser YT, Kratz AS, Bernhardt K, Fink S, Mizani T, Lin X, Jauch A, Mautner J, Kopp-Schneider A, Feederle R, Hoffmann I, Delecluse HJ
Get in touch with us

