Molecular Embryology
- Cell and Tumor Biology

Prof. Dr. Christof Niehrs
Division Head
How cells communicate with their environment via cell-cell interactions and by growth factors is a key question in the molecular life sciences, including tumor biology. Wnt signaling plays an important role in embryonic development and cancer. In the Division of Molecular Embryology we study mechanisms of Wnt pathway regulation. To this end, we identify developmental control genes, investigate what their biological role and biochemical mode of action is, and how the genes are regulated.
Lines of Research:
In processes ranging from larval development to respiration, mucociliary membranes defend epithelia against irritants and pathogens by a directional mucous flow generated through the coordinated beating of motile cilia. Deficiency of these nanopropellers leads to airway disease and ciliopathies, and understanding their cell biology is important for the rational design of cilio-stimulatory therapies. Hence, understanding their cell biology is important for the rational design of cilio-stimulatory therapies.
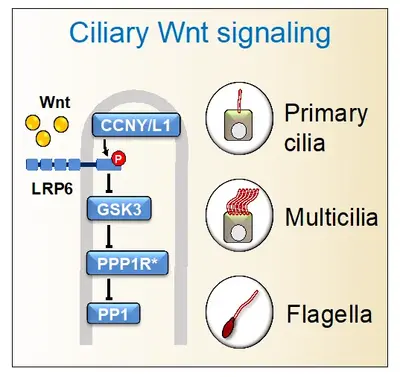
Cilia and Wnt signaling have a complex relationship, wherein Wnt regulates cilia and, conversely, cilia may affect Wnt signaling. Recently, we showed that Wnt receptors are present in flagella, primary cilia, and multicilia, where they transmit an intraciliary signal that is independent of β-catenin. Intraciliary Wnt signaling promotes ciliogenesis, affecting male fertility, adipogenesis, and mucociliary clearance. Wnt also stimulates the beating of motile cilia, highlighting that these nanomotors too, are chemosensory. Intraciliary Wnt signaling employs a Wnt- protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) signaling axis, involving the canonical Wnt pathway's inhibition of GSK3 to repress PP1 activity. Collectively, these findings support that cilia are Wnt signaling organelles, with implications for ciliopathies and cancer.
Our working hypothesis is that Wnt ┫PP1 signaling is physiologically relevant in other mammalian ciliated cells and tissues. To answer in which physiological processes and tissues does primary and mucociliary Wnt signaling play a role in e.g. mouse, we need to deconvolute the requirement for Wnt signaling in the plethora of other tissues and processes wherein the pathway is involved from those where specifically ciliary Wnt signaling is involved. Towards this end we are studying mouse mutants in which components specific for ciliary Wnt signaling are inactivated.
References
- Zhang K, Da Silva F, Seidl C, Wilsch-Bräuninger M, Herbst J, Huttner WB, Niehrs C. (2023) Primary cilia are WNT-transducing organelles whose biogenesis is controlled by a WNT-PP1 axis. Dev Cell 58:139-154.
- Seidl C, Da Silva F, Zhang K, Wohlgemuth K, Omran H, Niehrs C. (2023) Mucociliary Wnt signaling promotes cilia biogenesis and beating. Nat Commun. 6; 14:1259.
- Niehrs C, Da Silva F, Seidl C. (2024) Cilia as Wnt signaling organelles. Trends Cell Biol. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2024.04.001
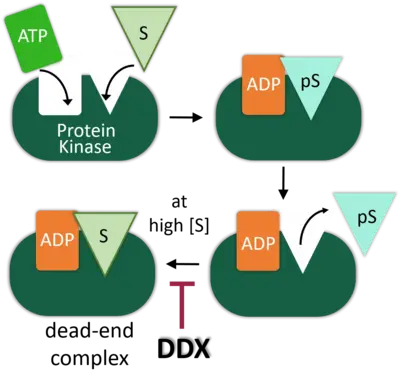
DEAD-box (DDX) RNA helicases are a large family of ATPases, many of which have unknown functions. We previously identified the DEAD-box RNA helicase DDX3 as a regulator of the Wnt-β-catenin network in embryonic development, where it acts as a regulator of Casein kinase 1 epsilon (CK1e). DDX RNA helicases commonly promote RNA processing, but intriguingly, the DDX3X oncogene is as we showed also an activator of Casein kinase 1e (CK1e) in Wnt signaling.
We demonstrated that kinase stimulation is a latent property of many DDX proteins. Stimulation resides in the helicase core domain and engages RNA binding- but not catalytic motifs. In DDX3X, the C-terminus provides specificity for DVL2 condensates in Wnt/CK1esignaling. For Casein kinase 2 (CK2a2), we identified DDX1, -24, -41, and -54 as physiological activators. Mathematical modeling of enzyme kinetics and stopped-flow spectroscopy converge on the conclusion that DDX proteins function as nucleotide exchange factors to stimulate CK2a2 activity and overcome substrate inhibition. Our studies reveal protein kinase stimulation by nucleotide exchange as a new principle in kinase regulation and an evolved function of DDX proteins.
We conducted several large-scale screens to investigate if protein kinase-DDX interaction is a more widespread phenomenon. In these screens, we retrieved Ser/Thr protein kinases as prominent interactors of DDX/DHX proteins and found hundreds of binary interactions. We extracted members of eleven protein kinase families, which bind to- and are stimulated by DDX proteins, including CAMK, CDK, CK1, CK2, DYRK, MARK, NEK, PRKC, SRPK, STE7/MAP2K, and STE20/PAK family members. MARK1 was identified in all screens and enzyme kinetic validation confirmed DDX proteins as V-type activators of MARK1. The findings indicate pervasive interactions between protein kinases and DEAD box RNA helicases and they will provide a rich resource to explore their regulatory relationships.
Our working hypothesis is that the interaction between DDX proteins and protein kinases will be particularly important in phase separation where protein concentrations are very high. We therefore investigate the role of DDX3X in biomolecular condensates during Wnt signaling.
References
Cruciat CM, Dolde C, de Groot RE, Ohkawara B, Reinhard C, Korswagen HC, and Niehrs C. (2013). RNA helicase DDX3 is a regulatory subunit of casein kinase 1 in Wnt-β-catenin signaling. Science 339, 1436-1441.
Fatti E, Hirth A, Švorinić A, Günther M, Stier G, Cruciat CM, Acebrón SP, Papageorgiou D, Sinning I, Krijgsveld J, Höfer T, Niehrs C. (2023) DEAD box RNA helicases act as nucleotide exchange factors for casein kinase 2. Sci Signal. 25;
Hirth, A., Fatti, E., Netz, E., Acebron, S.P., Papageorgiou D., Švorinić, A., Cruciat, C.-M., Karaulanov, E., Gopanenko, A., Zhu, T., Sinning, I., Krijgsveld, J., Kohlbacher, O., Niehrs, C. (2024) DEAD box RNA helicases are pervasive protein kinase interactors and activators. Genome Res. doi: 10.1101/gr.278264.123.
R-Spondins (RSPO1-4) are a family of four secreted proteins implicated in development and cancer, which we have discovered in 2004 as Wnt agonists. RSPOs function by protecting WNT receptors from ubiquitination and degradation by the E3 ubiquitin ligases ZNRF3/RNF43. RSPOs became famous as a key ingredient to maintain organoid cultures where they stimulate stem cell growth. We are investigating the molecular mechanism of RSPO signaling as well as its biological roles during embryonic development. Recently, we found a pivotal role of RSPO2 in development of the Left-Right (LR) body axis.
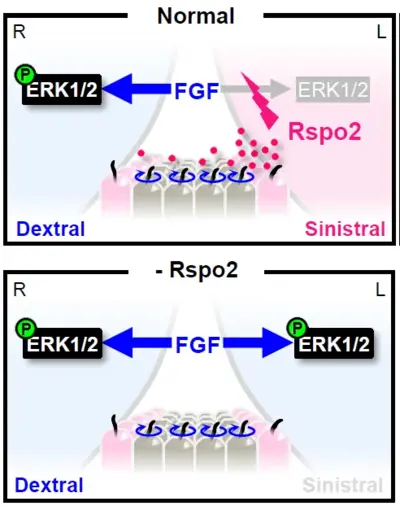
How animals establish the LR axis, is a fundamental problem in biology, as it serves as the basis for the formation of all subsequent LR-asymmetric structures. LR asymmetry is regulated by the left-right organizer (LRO) where LR symmetry breaking takes place. Defective LRO formation results in heterotaxy (HTX), congenital diseases ranging from organ malformation to misarrangement of organs across the LR axis, notably congenital heart defects. The LRO harbors motile cilia, which rotate clockwise to generate a leftward fluid flow.
We discovered in Xenopus embryos, that rspo2 acts in the LRO as a LR morphogen. Rspo2 is expressed in the LRO and it is necessary and sufficient for organ laterality and LR specification. Specifically, Rspo2 acts as sinistralizing (determining Left-specific cell fate) signal and operates upstream of the well-established Nodal-Pitx2 cassette, which is essential for sinistral fate. Surprisingly, in LR patterning Rspo2 acts as an FGF receptor antagonist. Rspo2 via its TSP1 domain binds Fgfr4 and promotes its membrane clearance by ZNRF3-dependent endocytosis. Concordantly, FGF signaling acts dextralizing (determining Right-specific cell fate) and forms a MAPK signaling gradient across the LRO. This FGF signaling gradient is high on the dextral- and low on the sinistral side. We are currently analyzing the LR signaling cascades downstream of RSPO2 and FGF as well as the evolutionary conservation of this mechanism in mouse.
We recently showed that RSPO2 and RSPO3 are also BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) antagonists. Specifically, RSPO2 is a high affinity ligand for the BMP receptor BMPR1A. RSPO2 forms a ternary complex between BMPR1A and the E3 ligase ZNRF3, which triggers endocytosis and degradation of the BMP receptor. We showed that Rspo2 antagonizes BMP signaling during embryonic axis formation in Xenopus. Moreover, we found that this novel function of RSPO2 as BMP antagonist also plays a critical role in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): AML cells secrete RSPO2 to promote their self-renewal and prevent cell differentiation. RSPO2 expression is generally elevated in AML patients with poor prognosis and inhibiting RSPO2 prolongs survival in AML mouse xenograft models.
Thus, RSPOs are multimodal modulators of growth factor signaling pathways, i.e. they can affect several receptors families (Wnt (ON) – BMP (OFF) – FGF (OFF)). Hence, we suspect even more target pathways and investigate the full repertoire of RSPO target receptors.
References
Lee H, Seidl C, Sun R, Glinka A, Niehrs C. (2020). R-spondins are BMP receptor antagonists in Xenopus early embryonic development. Nat Commun. 11:5570.
Sun R, He L, Lee H, Glinka A, Andresen C, Hübschmann D, Jeremias I, Müller-Decker K, Pabst C, Niehrs C (2021) RSPO2 inhibits BMP signaling to promote self-renewal in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Rep.36:109559.
Lee H, Camuto CM, Niehrs C. (2024) R-Spondin 2 governs Xenopus left-right body axis formation by establishing an FGF signaling gradient. Nat Commun. 2;15:1003

Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is a rapidly progressing field that has broadened the scope of therapeutic targets to include historically undruggable proteins and overcome drug resistance. In contrast to degradation of cytosolic targets, the TPD toolbox to target extracellular proteins is rather limited. To overcome this limitation, we took advantage of R-spondin's ability to target diverse cargo to degradation and developed ROTACs (R-spondin Targeting Chimera). ROTACs are bispecific WNT- and BMP signaling-disabled R-spondin chimeras, which leverage the specificity of these stem cell growth factors for ZNRF3/RNF43 E3 transmembrane ligases to target transmembrane protein degradation.
As proof of concept, we targeted the immune checkpoint protein programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1), a prominent cancer therapeutic target, with a WNT- and BMP signaling-disabled bispecific RSPO2 chimera, R2PD1. R2PD1 binds PD-L1 and at picomolar concentration induces its lysosomal degradation. In melanoma cell lines, R2PD1 induces between 50-90% PD-L1 protein degradation. Moreover, R2PD1 reactivates cytotoxic T cells and inhibits tumor cell proliferation more potently than Atezolizumab, a well-established PD-L1 in clinical use. We suggest that signaling-disabled ROTACs represent a paradigm to target cell surface proteins for degradation in a range of applications. Hence, signaling-disabled RSPO chimeras represent a novel avenue to target cell surface proteins for degradation. We currently develop novel ROTACs for targeted cancer therapy.
References
Sun R, Lee H, Niehrs C (2023) ROTACs leverage signaling-incompetent R-spondin for targeted protein degradation. Cell Chem Biol. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.05.010.
Team
-

Prof. Dr. Christof Niehrs
Division Head
-
Diptanshu Banerjee
-

Dr. Katja Baur
Postdoctoral Scientist
-

Celine Camuto
Doctoral Researcher
-
Nicolas Garcia Munoz
-

Dr. Tianshu Gui
Postdoctoral Scientist
-

Jessica Herbst
Technician
-

Dr. Nedasadat Kazemeinjasemi
Postdoctoral Scientist
-

Dr. Hyeyoon Lee
Postdoctoral Scientist
-

Dr. Romina Ines Minen
Postdoctoral Scientist
-

Carmen Reinhard
Technician
-

Angelika Schmidt-Zitouni
Secretary
-
Dr. Lars Schomacher
Postdoctoral Scientist
-
Samia Schwab
-

Tianheng Zhu
Doctoral Researcher
Job Opportunities
Masters, PhD, and Postdoc positions available:
Motivated students with a strong success record and solid background in cellular and molecular biology are encouraged to apply via email to Christof Niehrs (niehrs@dkfz.de). Please send your CV with grades, a list of publications, a description of research interests, and the email addresses of two referees.
Lab Practicals & Internships:
We are offering lab practicals for students holding at least a BSc degree in all domains of our research (see our Research). You will be supervised by a postdoc or advanced PhD student. To be productive, the minimum duration of Lab Practicals & Internships is 6 weeks.
Selected Publications
R-Spondin 2 governs Xenopus left-right body axis formation by establishing an FGF signaling gradient
Lee, H. et al.
Sun, R. et al.
Zhang, K. et al.
Cruciat, C.M. et al.
Get in touch with us


